I think we can all agree we’re in an AI revolution. Everywhere, in almost every branch of making, doing and conducting business, artificial intelligence is having an impact. Already past the stage of adoption, AI technologies have matured fast. Depending on your industry, AI tools either provide a competitive edge – or they’re necessary simply to compete.
More than 75% of respondents in the 2025 McKinsey State of AI survey reported that their organization was regularly using generative AI – artificial intelligence that creates new content (up from 65% in 2024). Businesses are also using AI in more functions than ever before, with over 40% using gen AI in more than two areas. And crucially, those using AI are reporting lower costs, and increased revenue.
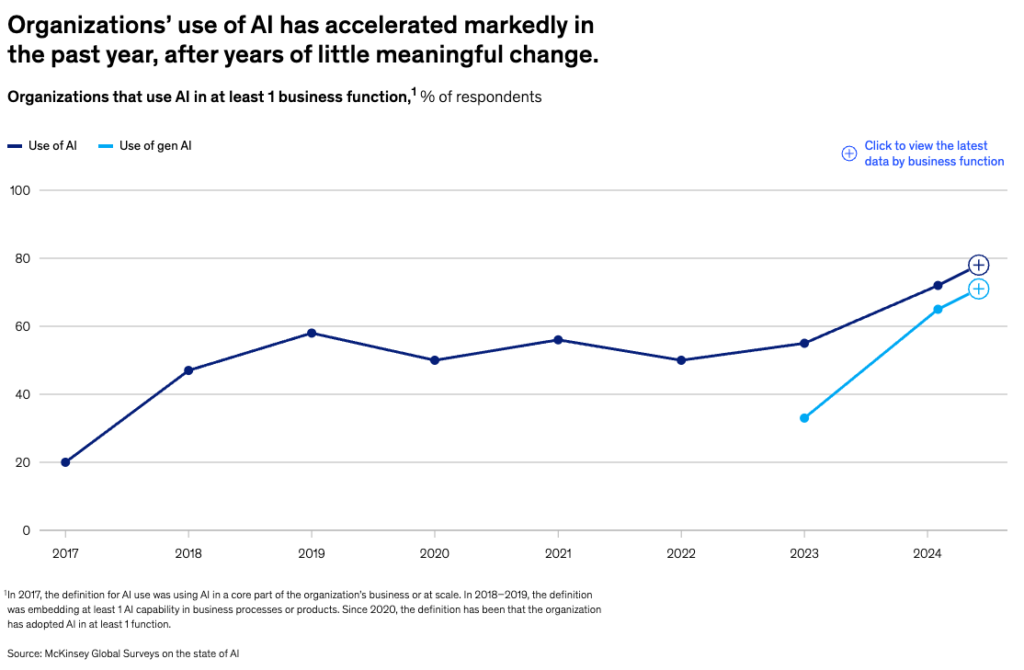
Artificial intelligence doesn’t need hype, the sheer number of industries it’s disrupting speaks for itself. From multimodal customer support in retail and ecommerce, to real-time product localization in global marketplaces, to AI‑assisted compliance translation in finance and healthcare, AI is now embedded in the operational fabric of countless industries.
Accelerated, automated AI systems can benefit any brand, but they’re particularly revolutionary for those who do – or who want to do – business globally. AI-powered translation tools are already enabling translation at scale, and supporting on-demand operations like customer service across multiple regions.
What’s changed?
It’s almost hard to process what’s changed in global communication, and how quickly. Just 20 years ago, translation was overwhelmingly manual, and doing business globally relied on multilingual employees and skilled translators. Localization—the process of adapting products, marketing, and strategies to different languages and cultures—was traditionally a bottleneck, restricting the pace at which products, marketing and strategies could be adapted, and putting a brake on businesses’ time to market.
Technology soon began to transform the way translation was done. Early machine translation (MT) models in the 2000s offered the first glimpse of automation, but quality was limited, The adoption of neural networks in 2015 marked the first real leap in translation quality. Today, AI translation is now powered not just by NMT, but by large language models (LLMs) and emerging large reasoning models (LRMs) that bring cultural, contextual, and domain-specific intelligence to outputs.
Adaptive NMT combined with LLM or LRM layers can reason about context, select the right tone, and adjust on the fly to brand glossaries or industry-specific terminology.
On the frontier, tools like SEAMLESSM4T and Hibiki are delivering real-time, multimodal translation—merging speech, text, and even live video captioning in one continuous pipeline. This evolution is shifting translation from a static, post-production step into a live, integrated layer of global communication.
Already fast and reliable, more recently, AI-based translation (By ‘AI translation,’ we mean translation work powered by advanced AI algorithms—often neural machine translation engines—capable of processing and converting text between languages with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
These AI-driven tools adapt to context, handle idiomatic expressions, and continually improve as they process more data. ) engines have gained a greater understanding of the nuance and context of language, producing higher quality results. MT is also becoming faster and more efficient. And when implemented in a translation management system (TMS), it’s also far more accessible than manual translation, and far easier to integrate into automated and semi-automated workflows.
Most recently, the power of AI has helped services move beyond the translation of static texts, into dynamic, real time translation. Users can choose to convert typed text, or spoken conversations in multiple languages.
For example, in a multinational Teams meeting, an English speaker’s comments can be instantly captioned in Japanese or French, allowing participants to listen in one language and read in another. On the research frontier, Meta’s SeamlessM4T model delivers real-time translation whether converting speech to text, speech to speech, or text using a single AI system, while Phrase Studio extends the principle to audio and video: a recorded product demo can be automatically transcribed, subtitled, and dubbed into more than 20 languages, giving every regional sales team a localized version ready to share the next day.
When combined with technology such as Augmented Reality, translated text can even be superimposed onto a source image, providing a far more dynamic way for users to interact in a foreign language.
Removing the barriers
For businesses, the benefits are real, and easily quantifiable. Enabled by AI, accurate machine translation is removing the bottlenecks to operating internationally. Brands can now create multilingual content at scale, accelerating delivery, and facilitating the exchange of ideas and information between international colleagues. Communicating with regional teams is easier, quicker, and less prone to misunderstanding.
55% reduction in post-editing, 100% match quality for short sentences, and less than two weeks’ deployment time – see how Phrase was tailor-made for this fashion house’s multilingual content challenges.
Machine translation is helping businesses rely less on manual translation, allowing skilled linguists and multilingual staff to focus on higher-value, specialize content.
On the one hand, that’s a cost saving, but it also speeds up global operations. Streamlined and automated workflows allow businesses to scale and flex their operations, calling up huge translation bandwidth when it’s needed, and quickly dropping it when it’s not.
Even with these advances, AI translation brings new challenges alongside its benefits. Sensitive and regulated data must be handled within robust governance frameworks, meeting privacy and compliance requirements that vary across industries and regions.
Hybrid NMT/LLM models can occasionally “hallucinate,” introduce subtle biases, or misinterpret cultural nuance—issues that become more pronounced in low‑resource languages or highly specialized domains.
Many organizations also face a workforce readiness gap, with insufficient change management plans to integrate AI into established workflows. And while automation accelerates delivery, businesses must still weigh security trade‑offs between the scalability of cloud processing and the control of on‑device or private‑cloud solutions.
As AI translation continues to improve, it further lowers the barriers to operating internationally, and reduces costs for doing so. With a language technology platform like Phrase, AI can learn preferred styles and tone of voice, helping ensure brand and messaging consistency between projects and locations. Removing time-consuming and costly mistakes further streamlines the workflow and enables teams to deliver content more efficiently at scale .
The real breakthrough: growth
For established businesses, the result is reduced costs, greater efficiency and – simply – better multilingual content. But AI translation can act as an accelerator to any brand with global ambitions. Businesses can be global from day one, massively widening their market without incurring correspondingly huge costs.
“Phrase allows our project managers to focus their efforts on core tasks, ensuring optimal productivity and resource allocation.”
Discover how Phrase helps BlaBlaCar optimize its localization budget.
Reducing translation costs brings benefits beyond efficiency. Money saved on manual translations can be reinvested into expert oversight. Translators are freed from repetitive tasks so they can bring their skills to bear on improving the quality of your messaging.
Experts can focus on the nuance and subtleties of a project, making sure the result strikes exactly the right note in the target market. That brings additional benefits from reduced support costs, as customers face fewer challenges in navigating touchpoints to achieve their goals.
AI still isn’t perfect, and it’s unlikely to ever be a full replacement for the skills and intuition of seasoned translators.
This is where human expertise comes in. Rather than fully replacing skilled linguists, AI translation works best in a ‘human-in-the-loop’ workflow. Translators and editors review AI outputs, refining the tone, ensuring cultural relevance, and making sure the final text resonates with the target audience. This model is now the standard in high‑performing localization teams, with AI handling the scale and speed while human experts ensure accuracy, cultural resonance, and brand consistency.
What has fundamentally changed is the opportunity.
By removing cost and speed barriers, AI makes it easier for new businesses to expand internationally and gives established companies the agility to adapt, innovate, and reach customers faster. The real advantage is not just more translation, but greater growth; the ability to test new markets, launch ideas globally, and deliver consistent experiences at scale.
Understanding AI in Localization: A Phrase Glossary
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the way businesses approach translation and localization, but terms like “AI,” “machine translation,” or “language models” can mean very different things depending on context.
This short glossary is designed to clarify the specific technologies and concepts we refer to across the Phrase platform, and on our blogs, product materials, and communications.






