Global business
Multilingual SEO: How to Reach International Audiences through Organic Search
The internet has created a vast playing field for businesses—one where competition is global. With so much choice at their fingertips, 9 out of 10 consumers will ignore your product if it’s not in their native language.
Making your website available in multiple languages is an important first step to increasing your product’s global reach. However, for your website to be noticed by as many diverse international audiences as possible, you need to put some thought into multilingual SEO (search engine optimization) as well.
Multilingual SEO is an essential tool for successfully marketing your product globally. This comprehensive guide will reveal effective SEO strategies for your global website, address common challenges, and explore how translation and localization technology can help you make the most of it.
What is multilingual SEO?
The internet has made the world a global village, enabling businesses to expand their customer base beyond geographical boundaries. However, to truly connect with diverse audiences, your website needs to speak their language—both literally and figuratively. This is where multilingual SEO comes into play.
Multilingual SEO is the process of optimizing website content in multiple languages to improve its visibility in search engines in diverse target markets.
It goes beyond simple translation and requires a deep understanding of the target audience, their search behavior, and local cultural nuances. With this level of depth, multilingual SEO can help you attract users from different language backgrounds, ultimately driving more organic traffic and increasing your online visibility.
When you consider that 60% of all Google search queries are in English, international businesses need to make sure they’re not missing out on the other 40%. By not properly optimizing their site for foreign languages, they could be losing out on a lot of traffic and potential customers.
Global brands like Coca-Cola and Nike have long recognized the importance of multilingual SEO in reaching their international customer base. By optimizing their websites for various languages, they could not only expand their reach but also position themselves as global players in their respective industries.
Big brands don’t just translate—they gain an in-depth understanding of their audiences in every target market and localize content to resonate and rank well locally.
DIVE DEEPER
What is localization, and why does it matter?
Find out why localization isn’t the same as translation and how it can support companies in expanding the global footprint of their business.
Benefits of implementing multilingual SEO
Employing effective multilingual SEO strategies unlocks a range of advantages for global businesses:
Localize content
Firstly, multilingual SEO allows you to tap into new markets and target customers who prefer to browse and make purchases in their native language. By providing localized content, you demonstrate a commitment to understanding and meeting their unique needs.
Improve user experience
Additionally, multilingual SEO improves user experience by displaying relevant content, localized search results, and language-specific metadata, which enhances customer satisfaction and builds brand loyalty.
Boost credibility with search engines
Notably, multilingual SEO strengthens your website’s authority and credibility in the eyes of search engines. When you optimize different language versions of your website, you are essentially signaling to search engines that you are a reliable source of information for multiple languages, increasing your chances of ranking higher in search results in different languages.
Demonstrate cultural understanding
Moreover, multilingual SEO allows you to leverage the power of cultural nuances. You can tailor your content to specific languages and cultures to effectively connect with your target audience on a deeper level. This level of personalization demonstrates your understanding and appreciation of their cultural values, traditions, and preferences, which can significantly enhance customer trust and loyalty.
Grow visibility
Another benefit of multilingual SEO is its impact on social media engagement. Optimizing your website for different languages increases the likelihood of your content being shared across various social media platforms. In turn, this can increase brand visibility, reach a wider audience, and ultimately, create more opportunities for customer engagement and conversions.
What is website localization?
Website localization goes beyond translation, fully adapting your site to the language and culture of diverse target markets. Learn more about how to make it work effectively.
Implementing an effective multilingual SEO strategy
To effectively harness the power of multilingual SEO, a strategic approach is essential:
- Identify your markets: It all starts with identifying the markets you wish to target.
- Conduct keyword research: Once you’ve pinpointed your chosen countries, conducting comprehensive keyword research becomes paramount. Understanding the search behavior and popular search terms in each language will allow you to tailor your website content to match user intent.
- Choose your URL structure: With the target languages and keywords in hand, the next step is to decide on your URL structure. Creating a user-friendly and easily comprehensible structure ensures a seamless experience for your international visitors.
- Localize your content: Now comes the crucial task of localizing your content. This process goes beyond word-for-word translation, as it involves adapting your blog posts, landing pages, or videos to resonate culturally and linguistically with your diverse audiences.
- Use hreflang tags: To signal the language targeting of each page to search engines, implementing hreflang tags is vital. This helps prevent duplicate content issues and ensures the correct pages show up in the appropriate search results for each region.
- Build backlinks: Lastly, building backlinks from reputable sources in each target market will boost your website’s authority and visibility in search engines.
Let’s take a look at each of these steps in greater detail and some real-life examples so you can make the most of your effort.
Step 1: Identify your target markets
Before embarking on a multilingual SEO strategy, it’s crucial to identify the specific markets you want to target. Conduct thorough market research to determine which countries or regions have the most potential for your business expansion. Consider factors such as market demand, competition, and cultural fit.
For example, let’s say you run an ecommerce website selling handmade jewelry. Through market research and understanding customer needs, you find that there’s a growing interest in artisan jewelry in Germany, France, and Japan. These countries will be your target markets for your multilingual SEO strategy.
Target audience analysis
People in different markets have different user habits, which means they expect different things from the websites they visit.
For example, the UAE has a mobile internet penetration rate of 95%, while in India only 32% of people report owning a smartphone at all. So your UAE and Indian versions of the website should approach mobile optimization differently.
Other aspects that can differ from country to country are the median age of the population, their level of education, and even internet speed. All these factors can influence how people interact with your website and what they expect from it
Pew Research Center provides some interesting data on internet usage around the world, which can be useful for understanding user habits in different markets.
Competitor research
Your competitors are targeting the same market as you, so a shortcut to understanding what works in that market is to look at what they’re doing. This includes everything from the topics they write about and how they optimize their website for different user habits to the backlinks they have and where those links come from.
Competitor research can be done manually by looking at their website and social media accounts, or by using a tool like Semrush or Ahrefs to understand their SEO and link-building efforts.
Nonetheless, keep in mind that to beat your competitors in their home field, you need to be one step ahead of them—so don’t just copy what they’re doing. Always try to find ways to improve on it.
For example, if your competitor is targeting a certain keyword and ranking quite high for it, but their content isn’t very comprehensive, you could write a longer and more detailed article on the same topic to outrank them.
Naturally, you’d first need to conduct keyword research to make sure that the keyword you’re targeting is actually worth going after—so let’s look at that next.
Step 2: Conduct comprehensive keyword research
Once you’ve chosen your target markets, conduct keyword research in each language to understand the search behavior of your potential customers. The goal is to find keywords that have a high enough monthly search volume to be worth targeting, but not so much competition that it would be difficult or expensive to rank for them.
Look at your existing organic website traffic
If your website is already multilingual, you can use Google Analytics to see which keywords are already bringing visitors to your site. This data can give you some ideas for new keywords to target. For example, if you sell shoes and see that people are already searching for “buy shoes online” in French, you might want to target that keyword.
Localize your target keywords
In the case of multilingual SEO, keywords used in one country or region might not be relevant in another. As different markets can use different keywords for the same product, you will likely need to adapt your keyword research process to each new market.
To keep using the artisan jewelry example, you use keyword research tools to find that in Germany, users frequently search for “handgemachter Schmuck” (handmade jewelry), “einzigartiger Schmuck” (unique jewelry), and “handgefertigte Ringe” (handcrafted rings). In France, popular search terms include “bijoux faits main” (handmade jewelry) and “colliers artisanaux” (artisan necklaces).
An easy way to find out how people in a new market search is by looking at Google Ads Keyword Planner, which shows you the monthly search volume for various keywords and phrases. Another useful tool is Google Trends, which lets you compare search volume for different keywords over time.
Rely on local SEO experts
When conducting keyword research in a new language, it can be tempting to use machine translation tools to quickly translate your target keywords into the new language.
While modern machine translation can be incredibly helpful for certain tasks, a human localizer’s judgment on whether a particular keyword or phrase will actually be used in a given market is still invaluable.
SEO experts with knowledge of the target market can help you figure out the user intent behind certain search queries. This will help you avoid targeting keywords that might get a lot of searches but not result in conversions.
Target local search engines in each market
Although Google is the most popular search engine in many countries, it’s not necessarily the only one. In some markets, there are other locally-popular search engines that you should target as well, such as Baidu in China or Yahoo! Japan in Japan.
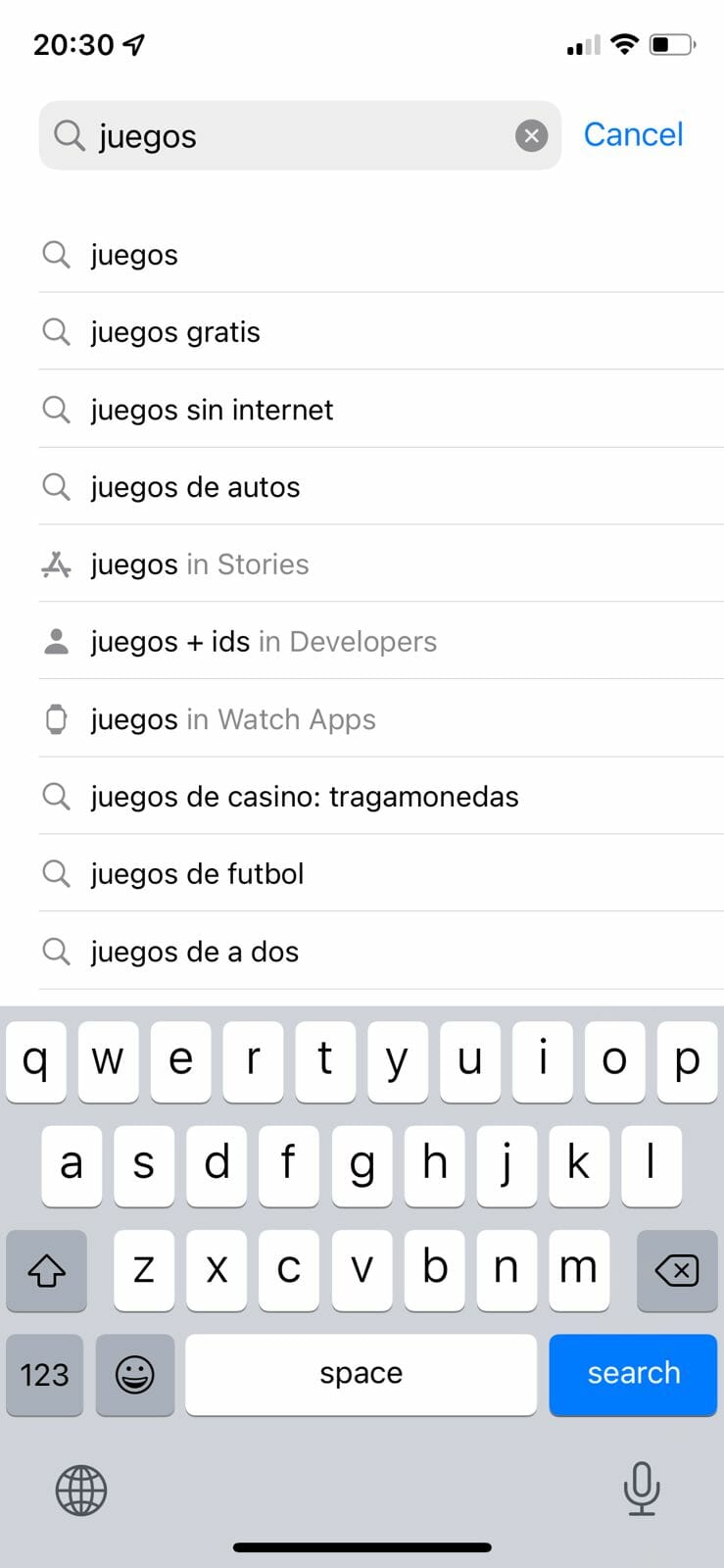
Optimize for app store search
If you have a mobile app, don’t forget about app store optimization—as most people use it to find new apps. You can do this manually by typing in a keyword and seeing what other suggestions pop up in the dropdown:
Step 3: Decide on your URL structure
Your website’s URL structure plays a vital role in multilingual SEO. It should be logical, user friendly, and indicate the language and region of each page. There are different URL structure options you can choose from. Here are the most common ones:
Country code top-level domains (ccTLDs)
If you need designated webpages for specific countries, having country code top-level domains (ccTLDs) may be the best solution. Domains like example.es and example.fr send signals to search engines that these sites should be served to users located in Spain and France.
However, as ccTLDs are separate domains, this strategy is typically the most expensive and time-consuming. Each ccTLD domain needs its own digital PR, content marketing, and link-building strategy. You also won’t be able to carry over any link acquisition efforts or domain authority acquired from off-site activity on other web pages.
Global top-level domains (gTLDs) in combination with subdomains
Global top-level domains (gTLDs) combined with subdomains like de.example.com enable improved geographical targeting and enhanced brand recognition in each target market. However, challenges arise from technical setup and maintenance complexity, as well as potential SEO alignment issues with subdomains.
gTLDs in combination with subfolders
If the location of your audience doesn’t have any impact on your products and services, you can use a single domain, and make use of subdirectories (subfolders) to host your designated language or country pages: example.com/es/.
These are typically used by businesses that want to target users in a single market with multiple languages being spoken. They also apply to geographical regions encompassing 2 or more countries that speak the same language, for example, Spanish-speaking Latin America.
gTLDs with a combination of subdomains and subfolders
gTLDs combined with subdomains and subfolders (es.example.com/es-mx/) allow for versatile site organization: While subdomains enable a more granular regional targeting, subfolders organize content within the main domain.
Benefits include enhanced targeted marketing and streamlined navigation, making websites more relevant to specific audiences. However, they’re quite complex to handle and have drawbacks to be aware of: cookie sharing, considerable server resources, long URLs, and potentially diluted SEO.
Given the benefits and drawbacks of each type of URL structure, you will want to carefully consider the needs of your business and your anticipated growth into new markets as you make your decision.
Step 4: Localize your content
One of the best ways to make your content relevant to a particular market is to write about topics that are specific to that market. This could be anything from local news and events to cultural differences or common problems people in that market face. Naturally, not all kinds of businesses and products will have locally relevant topics to write about.
Nevertheless, if you give a familiar piece of content a local touch, you stand a good chance of capturing the attention of the local audience.
For example, if you’re shipping software as a service (SaaS) for managing social media accounts, you’d want to have content focused on different social media platforms in different markets, e.g. Facebook and Twitter in the US, WeChat in China, etc.
Still, content creation in the target language from scratch can come with significant costs. An alternative strategy is to localize your existing content. Localization is about much more than mere translation. It requires adapting your website’s content to suit the cultural nuances and preferences of each target audience. This includes language, currency, images, product descriptions, and any other elements that resonate better with the local audience.
It’s not just about words, it’s about vibes. Make your site speak the language of your target audience—literally and culturally.
When localiazing multilingual content, it’s key to make sure that your original content is “internationalized” from the start. In other words, you should write content that is easy to localize. This means using simple language, avoiding idioms and slang, and making sure that even people who are not native speakers of your language can understand what you’re saying.
Translating content word for word may not always yield the desired results, as it can miss the mark when it comes to cultural relevance and resonance. For instance, a marketing slogan or a catchy phrase that works well in one language may not have the same impact when translated directly into another language.
In practical terms, this means that in Germany, you replace the English product descriptions with German ones, highlight the eco-friendly aspects of your jewelry (as Germans tend to value sustainability), and adjust prices to be displayed in euros. In France, you emphasize the elegance and fashion-forward aspects of your jewelry, and prices are shown in euros as well.
Use machine translation for content with low visibility
Machine translation tools are great when you need to quickly translate a document for informational purposes, or when particular website content has low visibility:
- Low-visibility or low-traffic content, such as internal documentation, website footers, social media posts for sentiment analysis, etc.
- Repetitive technical content that doesn’t need to be 100% accurate, just actionable, like instruction manuals
- User-generated content like product reviews, for which consumers generally expect low quality
- Quickly perishable content, like chat or email support messages, customer inquiries, etc.
- Large bulks of content with a short turn-around, such as hundreds of product descriptions that need to go live quickly
- Frequently amended content like feature and information updates
Apply light or full post-editing to more sensitive content
To produce high-quality content that will rank well in search engines and convert visitors into customers, machine translation is best coupled with post-editing by human experts who can adjust the output and localize the keywords. To make the most of it, make sure you hire professional translators who are native speakers of the target language and have a deep understanding of your industry.
You can aid the work of post-editors with traditional translation technology such as glossaries, termbases, and translation memories, as well as brand books and style guides. This will keep the brand voice and key messaging consistent across cultures and languages and is very feasible with MTPE.
As a general guideline, the following content types require post-editing:
- Product titles: They are highly informative and concise, they tend to contain proper names and polysemous words, and their word order is usually relatively free, which can cause ambiguity.
- Translations between language pairs of dissimilar syntax, like Japanese and Spanish, because the reordering of words and phrases to well-formed sentences becomes more challenging for machine translation engines.
- Product descriptions: They need to be well-crafted and clearly state the product’s features or benefits without room for ambiguity.
- Content of medium visibility that needs to be as accurate as possible: knowledge base, FAQs, alerts, etc.
- Back-end meta information such as image alt texts and captions: While their visibility is low, a human needs to ensure that the target-language keywords are present.
Rely on human translation and transcreation for marketing and promotional content
If you’re targeting a market whose culture is very different from your own, it might be difficult to make a translation—however good it is—achieve the same effect as the original. In such cases, it might be a good idea to employ transcreation, i.e., fully adapt your brand-sensitive, high-traffic, and durable content assets to the target market while still maintaining its core message and meaning.
Put another way, a human translator will need to recreate the message in the target language in a non-literal way. It’s the case of:
- Homepages
- Advertising landing pages
- Blog posts
- Newsletter campaigns
- Press releases
- SEO content
- Print advertising, etc.
Step 5: Implement hreflang tags
Hreflang tags are HTML attributes that inform search engines about the language and regional targeting of your web pages. This helps search engines display the correct version of your pages to users in different countries, reducing the risk of duplicate content issues and ensuring better user experience.
There are 3 options for placing hreflang tags:
In the <head> section of your HTML code:
<head>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en” href=”https://example.com/en/”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”de” href=”https://example.com/de/”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”fr” href=”https://example.com/fr/”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”es” href=”https://example.com/es/”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”ja” href=”https://example.com/ja/”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”zh-hans” href=”https://example.com/zh-hans/”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”zh-hant” href=”https://example.com/zh-hant/”>
<link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”ko” href=”https://example.com/ko/”>
</head>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)In the HTTP response header:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/pdf
Link: <https://example.com/whitepaper.pdf>; rel=”alternate”;hreflang=”en”,
<https://example.com/de/whitepaper.pdf>; rel=”alternate”;hreflang=”de”,
<https://example.com/fr/whitepaper.pdf>; rel=”alternate”;hreflang=”fr”,
<https://example.com/es/whitepaper.pdf>; rel=”alternate”;hreflang=”es”,
<https://example.com/ja/whitepaper.pdf>; rel=”alternate”;hreflang=”ja”,
<https://example.com/zh-Hans/whitepaper.pdf>; rel=”alternate”;hreflang=”zh-Hans”,
<https://example.com/zh-Hant/whitepaper.pdf>; rel=”alternate”;hreflang=”zh-Hant”,Code language: HTML, XML (xml)In the XML sitemap:
<url>
<loc>https://example.com/blog/sample-blog-article/</loc>
<xhtml:link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”en” href=”https://example.com/blog/sample-blog-article/”/>
<xhtml:link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”de” href=”https://example.com/de/blog/sample-blog-article/”/>
<xhtml:link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”fr” href=”https://example.com/fr/blog/sample-blog-article/”/>
<xhtml:link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”es” href=”https://example.com/es/blog/sample-blog-article/”/>
<xhtml:link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”it” href=”https://example.com/it/blog/sample-blog-article/”/>
<xhtml:link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”nl” href=”https://example.com/nl/blog/sample-blog-article/”/>
</url>Code language: HTML, XML (xml)The choice between the 3 options depends on the structure of your website. If you have a large website with many pages, it’s easier to manage hreflang tags in an XML sitemap. Managing them in the HTML code, though, makes it easier to change them if you need to. Finally, HTTP headers are a good option if the document in question doesn’t have HTML as such—say if it’s a PDF file.
Note that you don’t only specify the language of the current page but also that of all the other language/regional versions of the same page. This lets search engines know that the pages are different versions of each other. One of the benefits here is that they share the same ranking signals, so if one page ranks well in search results, the others will, too.
There are a lot of details to consider when using hreflang tags, so you might want to involve an SEO expert in the process before implementing them. This is especially important if your website is large and complex.
Step 6: Build backlinks from reputable sources in each target market
Backlinks are links from other websites to your own website. According to most sources, they’re among the highest ranking factors on search engines, so getting high-quality links from relevant websites is an essential part of a successful SEO strategy.
While your localized pages may enjoy some of the link equity from your main website, you may not rank much. This means finding websites that are relevant to the market you target and getting them to link to your localized pages.
For the German and French markets, for example, you need to collaborate with popular local fashion bloggers, influencers, and jewelry enthusiasts to create engaging content featuring your handmade jewelry. As these influencers link back to your website, search engines recognize the authority and relevance of your content in the respective markets, boosting your rankings in local search results.
Here are some of the most common and effective ways to make an “organic” case for other websites to link to yours:
- Creating great content that people want to link to (e.g., blog posts, infographics, etc.)
- Creating tools and resources that people want to link to (e.g., calculators, checklists, etc.)
- Getting involved in the community by writing guest posts or participating in forums and Q&A sites
- Creating partnerships with other websites in your niche or industry
- Getting featured on popular blogs and news sites (e.g., by writing a guest post)
None of the above may be as simple as making a few technical changes to your website. It requires a lot of hard work and dedication, but the benefits speak for themselves.
The greatest challenge in multilingual SEO—and how to overcome it
The journey towards multilingual SEO success isn’t without its hurdles. Mere translation of your website’s content may not be enough to establish a meaningful connection with diverse cultures and languages. To truly resonate with your target audience across borders, a well-thought-out localization strategy is key.
The greatest challenge in multilingual SEO lies in accurately adapting content to suit the nuances of different cultures and languages. A mere translation can often result in misinterpretations and a failure to connect with the target audience. Additionally, managing multiple language versions of your website manually can be a daunting and time-consuming task, potentially hindering your global growth potential.
This is where localization technology comes in. By leveraging cutting-edge localization software, such as the Phrase Localization Platform, global organizations can streamline the process of adapting and managing content across various languages seamlessly.
For example, adopting a translation management system is an effective way of getting managers, subject matter experts, translators, copywriters, marketers, and designers on the same page. Whether your team members are in the office, working from home, or outside, it makes no difference when working with a cloud-based TMS.
What is a translation management system?
Learn what makes a translation management system and how it helps businesses seeking to expand globally translate content more quickly and efficiently.
Moreover, a TMS will help you establish a clear translation and localization workflow, monitor the projects’ progress, and, most importantly, invite different departments and branches of your organization to get involved in the localization process.
A translation management system gets you out of the most intricate localization labyrinths with the following capabilities:
- Automation: Translatable content should be automatically extracted from content management systems, source code repositories, or marketing automation platforms and routed to the translation interface. Translated content should be able to be automatically imported back into the original environment.
- Centralization: Providing a single point of access to all relevant marketing materials, resources, instructions, and content increases productivity and reduces the chances of errors. Marketing and localization teams should be able to work from a single platform, with all the tools they need at their fingertips.
- Real-time collaboration: A TMS acts as a hub through which marketing teams can collaborate with other departments and both in-house and external stakeholders in real time, ensuring that everyone’s working from the most up-to-date content.
- Translation memory: A robust TMS lets you store translations in a cloud-based translation memory, which allows translators and marketing teams to reuse content across different marketing campaigns.
- Support for familiar file formats: No more copy-paste. You should be able to submit content for translation in your preferred file types: IDML, PSD, SVG, HTML, etc.
- Integration: The TMS should be able to quickly and easily integrate with content management systems (e.g., Marketo, HubSpot, Adobe Experience Manager, WordPress, Drupal, Contentful, Contentstack, Sitecore), ecommerce platforms, marketing automation platforms, and CRM systems, or even let you build a custom integration via a REST API.
- Quality control: The TMS should include a quality assurance process that facilitates checking translations for accuracy against previously translated content (through the use of translation memories), marketing brand guidelines, style guides, and glossaries.
- AI-powered machine translation: A modern TMS combines well-established translation technology with AI-powered machine translation capabilities.
- Tracking and reports: The best TMS will provide marketing teams with insights and reporting that can be used to improve marketing performance and marketing ROI and will let them monitor translators’ performance to make any necessary adjustments.
With technology firmly in place to support it, localization efforts are nearly unbeatable as a competitive advantage for any company seeking to unlock the potential of multilingual SEO. A robust TMS helps teams deliver higher quality work on time and on budget, which ultimately boosts marketing performance, increases sales, and boosts the return on investment.
Multilingual SEO is easier with the right strategy and technology
Multilingual SEO is one of the most powerful tools for global businesses to expand their global presence and connect with international audiences. Once you’ve effectively implemented multilingual SEO, your brand can benefit from stronger user experiences, better credibility, enhanced personalization for audiences, and more robust visibility.
With cloud localization technology, you can accurately adapt content and overcome the limitations of content that is merely translated. A robust translation management system streamlines the process of adapting and managing content across multiple languages seamlessly, helping businesses thrive within the ever-expanding global marketplace.
Phrase TMS
The enterprise-ready translation management system
Work with the leading TMS to automate translation workflows with cost control and quality checks.





