Translation management
How to Translate a Website: Top 3 Website Translation Methods to Use

Let’s do a quick thought experiment: Think of the website you visit the most. It could be a marketplace like Amazon or a social hangout like Facebook. Now, picture this: What if you couldn’t understand the language the website was created in—would it still be usable for you?
Chances are, for most of us, the answer tends to be negative. Even if a few words here and there might make sense, navigating foreign-language websites can quickly turn into a hassle. Thankfully, there are several methods available to effectively translate a website online.
Whether you’re a user trying to access content or a website owner aiming to expand reach, this guide will show you how to translate a web page in your preferred browser and on your mobile device—and even how to translate an entire website of your own step by step.
The right translation software for your needs
Drive global growth by automating, managing, and translating all your content with the world’s most powerful, connective, and customizable translation software.
3 key approaches to translating a website
To translate a web page, you first need to choose the right translation method for your needs. This might depend, for example, on how accurate you want the translation to be.
Let’s have a look at the 3 most common approaches to translating a site, what the pros and cons of each are, and how to implement them.
1. Human translation
One of the frequently used methods to translate a web page is to hire human translators to convert content from one language to another.
Professional website translation services have the advantage of being very accurate, as long as you find expert linguists who understand both the source and target languages well and who are familiar with the subject matter of the site.
On the flip side, human translation can often be costly, and it can take a while to get the translated pages back from the translator.
Advantages of human translation:
- High accuracy
- Understanding of context
- Can adapt to specific registers and tones
- Better understanding of the site’s purpose and how to communicate that to users in the target language
- Creativity—translators can come up with catchy phrases or turns of phrase that will resonate with users
- Can create SEO-friendly translations
Drawbacks of human translation:
- Often costly
- Time-consuming
- Prone to human errors like typos
- Potential to create bottlenecks when no translators are available
2. Machine translation
An alternative to human translation is machine translation (MT), which is where you use a computer program to translate the text on your site automatically. This has the advantage of being much faster and cheaper than human translation, but the downside is that it’s often not as accurate.
Benefits of machine translation:
- Fast
- Cost-effective
- Can be used for large projects
- Can be scaled up easily
- Can be post-edited for enhanced accuracy
Limitations of machine translation:
- Not suitable for all projects
- Lower accuracy
- Can’t adapt to specific registers or tones
- Not as fluent or natural-sounding as human translation
- Might need a lot of data to produce good results
- Typically unable to pick up on text nuances and idiomatic expressions
- Less creative than human translation
- Potential legal risks—if the translation is not accurate, it could be considered misleading and you could be liable for damages
While the disadvantages of machine translation might seem to outweigh the advantages, it’s important to remember that machine translation has come a long way in recent years with the emergence of neural machine translation (NMT), and it continues to improve.
NMT typically delivers impressive results, especially for common language pairs like English to German, and it’s increasingly difficult to catch grammatical or punctuation mistakes in the machine-translated text.
3. Machine translation post-editing (MTPE)
A third option, which is a hybrid of human and machine translation, is machine translation post-editing (MTPE). MTPE is where you use machine translation tools to generate a draft translation, which is then edited and polished by a human translator to improve accuracy.
In recent years, post-editing has become quite popular in the translation industry. This is also due to the fact that many resources are being invested in the development of the so-called “neural machine translation engines.”
To sum it up, simply weigh the pros and cons based on your objectives and choose the translation approach that best meets your needs. Now, let’s go ahead and put this into action.
How to translate a web page in your browser
Assuming you just need to quickly translate a foreign-language web page for your own personal use and don’t need to worry about accuracy, there are a few different ways you can do it right in your web browser.
Most web browsers, including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox, have built-in translation tools that can automatically translate web pages for you.
Naturally, the content displayed in the preferred language won’t be perfect. In some cases (like minority languages), the output quality may even be poor.
However, in most cases, even if the translation isn’t optimal and the cultural references are wrong, it’s still possible to understand the key points of the content.
Depending on your browser, you’ll usually see a dialog box asking if you want to translate the page when you come across a web page written in a foreign language. Alternatively, in just a few clicks, you can typically access the translation options in your browser’s settings.
How to translate a website in Google Chrome
Google owns one of the most popular automatic page translators, Google Translate. For this reason, using Google Chrome as a browser to carry out the automatic translation of websites is one of the most practical translation options.
Translating a page with Google Translate is quite straightforward:
- Open a website in any foreign language.
- Click on the Google Translate icon on the right in the address bar.
- Select the language in which you want to read the content.
- The content of the webpage will automatically appear in the selected language.
- If you wish, save your settings for the future—this will save you a lot of time.

How to translate a web page in Firefox
To translate the content of a website in Firefox, it is necessary to install specific add-ons. The installation is easy and quick. The best way is to use the Google Translate add-on because it is simple and user-friendly.
To install the Google Translate add-on and translate a web page in Firefox, follow the steps below:
- Launch the Mozilla Firefox browser.
- Visit the Firefox add-ons page and search for Google Translate.
- There are many options to choose from. In this case, we’ll go with “Simple Translate,” one of the best-rated ones, but feel free to try other extensions to find the one that works best for you.
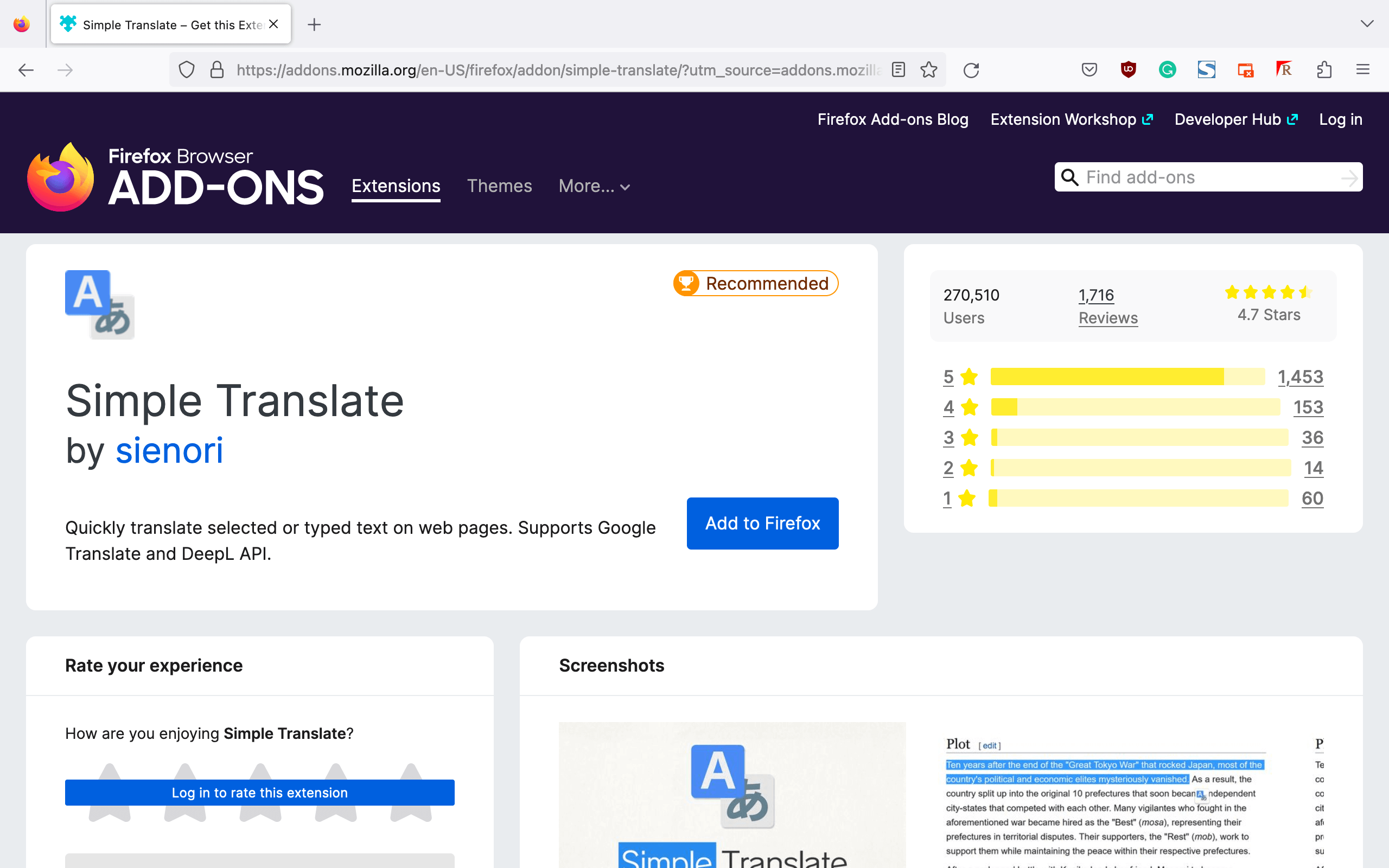
- Click on “Install” and follow the described steps to install the add-on.
- On the address bar, enter the link to the web page you would like to translate.
- Go to the Translate icon at the top right-hand corner shown by the letter ”T” and right-click on it.
- Select the option “Translate page with Google Translate.”

How to translate a web page in Safari
In Safari, it’s possible to use the Smart Search function to translate a site. Here is how to do it:
- Simply navigate to the website you need to get translated.
- Select the “A” button at the top right of the browser’s address bar.
- In the drop-down menu, you can select the language into which you wish to translate the content.
How to translate a web page on your mobile device
Most mobile browsers, just like their desktop counterparts, also offer automatic translation features. Let’s see how to do it in the 2 most popular operating systems: iOS and Android.
How to translate a website on iPhone
To translate a website using your iPhone, follow the steps below:
- Open the Safari browser (default) and click on the “aA” symbol in the address bar.
- A drop-down menu will open, and you should see the option “Translate Website,” which allows you to translate the content into any language available in the list.

There is also another way to translate websites on iOS devices, i.e., with Microsoft’s Translator, which you can download for free from the App Store:
- Open Safari on your iPhone while viewing a web page and tap the “Share” button.
- Scroll left and tap the “More” button. You will now see a Microsoft Translator option.
- Set it to the “on” position.
- Tap “Done.”
How to translate a website on Android
For those using the Chrome browser on an Android mobile device, the procedure to translate a website differs from the one used in the desktop version of the browser. Simply follow the steps below:
- Open the Chrome app and—when visiting a web page in another language—select “More” and the target language at the bottom of the page.
- Chrome will offer to translate the web page one time or to always translate it.
- Select the option that you prefer.

How to translate an entire website of your own
Up to here, we’ve dealt with manual methods of translating a page online. However, if you’re the owner of a website, you probably want to take some form of proactive action to ensure that your content is accessible to as many people as possible, regardless of language barriers.
And here’s where things can start to get complicated because a few clicks of a button is no longer enough. When businesses or organizations want to make their content available for multiple foreign markets, we no longer talk of translation but of localization.
Distinguishing between translation and localization
Contrary to popular belief, translation and localization don’t mean the same thing.
You can think of translation as a form of transposing written content from one language to another, respecting the original’s meaning and structure. The goal is to ensure that the text makes sense in the target language.
On the other hand, localization is a much more complex undertaking that goes beyond transposing written text. In other words, it’s much more than translating the website content (plain words) into the local languages of your target audiences.
DIVE DEEPER
What is localization, and why does it matter?
Find out why localization isn’t the same as translation and how it can support companies in expanding the global footprint of their business.
To ensure successful content localization for your website, you need to consider some additional factors:
- Cultural context: A website that is successful in one country might not work as well in another. It might be necessary to adapt the whole content to better suit the target audience.
- Technical considerations: This includes aspects such as hosting or domain names—you might need a local domain or host in the target country.
- Design: The overall UX and UI design of the website, including colors, layout, images, and videos are also important considerations. For example, you don’t want to use images with people from one culture on a website targeting another culture.
- Functionality: Localization might also require the website to be modified in such a way that certain functionalities, such as ecommerce or online payments, work as required in the target country.
- User experience (UX): Adapting the UX to local expectations is vital. What users from one culture expect from a website might be completely different from what users in another culture expect.
- Date, time, and currency formats: Depending on the target country, you might need to change kilometers to miles, for example, or adapt the date format to better suit the standards of the target market.
- Language variety: If you offer your website in French, for example, you should differentiate the variant according to the markets in which you operate, e.g. French (Canada), French (Belgium), French (France), and so on, because each country has its own conventions, style, and language variant.
Defining a clear localization strategy
Successful localization starts with a solid localization strategy. This implies having a good understanding of the target markets, as well as the needs and expectations of your website visitors, so they will take the desired action.
Some questions you can ask yourself to get started include:
- Who is your target audience?
- What are their needs and expectations?
- What type of devices do they use to access your website (e.g. desktop, mobile)?
- What is your budget for localization?
- Are you looking to target one specific market first or multiple markets simultaneously?
- What content will you prioritize? Based on what?
- Which tools and technologies will you use?
Once you’ve addressed these questions, you can start building a website localization strategy.
Use professional translation software to translate websites at scale
Relying on cloud-based translation technology is essential for ensuring that everything runs smoothly during the entire localization process.
More specifically, consider using a translation management system (TMS). This software platform combines machine translation with many different functionalities designed to automate various parts of the translation process—from importing and exporting content for translation to team collaboration.
The key components of a translation management system are:
- Computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools, such as translation memory and term bases
- AI-powered machine translation capabilities
- Project management features
- Workflow automation solutions
- Real-time collaboration capabilities
- Native integrations (e.g., a WordPress translation plugin to connect with your content management system)
- Advanced reports and analytics
- The possibility to upload and manage glossaries
- Quality assurance (QA) features to check the target content before publication, and more
The automation and other features provided by a cloud-based TMS enable you to free up time for other tasks, like researching topics or creating content, which are the more human-centric aspects of localization that demand more attention.
Phrase TMS
The enterprise-ready translation management system
Work with the leading TMS to automate translation workflows with cost control and quality checks.
What to look for in a translation technology provider
A robust, cloud-based translation solution, such as Phrase TMS, combines well-established technology that supports human translation (CAT tools) with AI-powered machine translation capabilities to streamline website translation projects.
Some TMSs even offer an AI-powered machine translation management feature that automatically selects the optimal MT engine for the user’s content.
This helps linguists, translation companies, and enterprise customers achieve better results with machine translation by dynamically integrating the process of engine evaluation and choice into existing workflows.
Furthermore, a TMS enables you to foster collaborative localization on a single platform to ensure a seamless and accurate website translation workflow for every team member involved.
A solid TMS provides out-of-the-box integrations to connect with existing tools within your digital ecosystem so you can automate as many of your multilingual web publishing as possible:
- Content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Contentful, Hubspot CMS Hub, Contentstack, etc.
- Marketing platforms like Adobe Commerce (previously Magento), Adobe Experience Manager, Hubspot Marketing Hub, or Marketo
- Storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and FTP
- Source code repositories like Bitbucket, Git, GitHub, and GitLab
- Documentation services (help centers and knowledge bases) like Salesforce Knowledge, Help Scout, and Zendesk
- Design software like Sketch and Figma
- Third-party services like Captionhub, Gengo, Gridly, LBS Suite, Paligo, Plunet, TransPDF, and XTRF
- Once you’ve chosen the TMS that best suits your needs, you can start the process of localizing your content into new languages and markets
Translating a website can be easier than you’d think
Regardless of whether you want a simple basic translation while browsing the web or you want a comprehensive website translation for your CMS system, there are many solutions available out there, for every budget and every need.
From free browser features or add-ons to comprehensive localization software with several useful features and professional human localization services, everything is possible. Just take your pick.
Speak with an expert
Want to learn how our solutions can help you unlock global opportunity? We’d be happy to show you around the Phrase Localization Platform and answer any questions you may have.




