Translation management
Translation Technology: A Look at Its Past, Present, and Future
Translation technology has been around for more than 5 decades now, but as our world has become increasingly interconnected, it’s only grown more essential.
A report by Nimdzi Insights found that the current language technology landscape includes more than 700 solutions. Given this diversity, how do you find a translation tool that best suits your business needs?
The first step is to gain a solid understanding of what translation technology is and how you can leverage it for international business. Keep reading to find out.
Unlock global business with the Phrase Localization Platform
Expand into new markets with all the tools you need in one technology suite for high-quality, fast, and scalable localization.
What is translation technology?
Translation technology is the use of software tools to facilitate the conversion of text from one language to another.
Translation technology encompasses:
- Computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools
- Machine translation (MT) software
- Translation management systems (TMS)
As is the case of most work aided by technology, translation technology tools can increase productivity, efficiency, and overall effectiveness in managing multilingual content for different target markets.
Before the emergence of translation technology, translation was done manually, with translators consulting paper dictionaries and using their best judgment.
The negative impact on business was substantial as a result of delayed time to market, general loss of consistency across content, high costs of inefficient operations, and lower output quality resulting from having to manually check for errors.
The birth of translation technology changed it all.
The history of translation technology
Some of the techniques used in modern translation technology can be traced back to the 9th century when an Arabic cryptographer named Al-Kindi developed the method of frequency analysis that is still used today. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century, when computers became available and affordable, that translation technology truly began to take shape.
Translation technology evolution in short
1950s: Georgetown University and IBM introduced the world’s first machine translation (MT) system. The approach was rule-based and lexicographical, which means that it relied on pre-programmed rules and dictionaries. Although this early form of MT proved unreliable and slow, it was still revolutionary—a stepping stone on the path toward more advanced technology.
1970s: The United States Department of Defense and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) started developing speech recognition technologies that paved the way for voice-to-text technologies.
1980s: The arrival of electronic dictionaries and terminological databases during this decade was another major turning point. These tools helped to make translation more accessible by providing translators with instant access to information (terminology with its translation) that could be used during the project.
Mid-1980s: The precursors of modern translation management systems (TMS) entered the scene from the hand of Coventry Lanchester Polytechnic University and its ALP System.
Late 1980s to early 1990s: IBM researchers introduced statistical machine translation (SMT). These systems were word-based and trained to translate one language into another by comparing large amounts of parallel texts in both languages (bilingual corpora). For example, they would analyze how often the German phrase “das auto” was translated as “the car” vs “the vehicle” vs “the automobile”, and choose the most frequent translation for the text at hand.
Early 1990s: Most commercial computer-assisted (or aided) translation (CAT) tools appeared during this decade—a milestone that transformed translation technology forever. It enabled a whole new generation of translators to work more efficiently and effectively.
Late 1990s: A new version of IBM’s statistical translation engine, this time phrase-based instead of word-based, was released. It became the commercial standard for years to come until Google entered the fray in 2006 with their neural machine translation (NMT) technology.
Early 2000s: The first cloud-based TMS solutions appeared in the market, enabling translation teams to work more flexibly and collaborate with other company members regardless of location.
2006: Google launched Google Translate—still statistical—which took the world by storm. The system first translated the input text into English before translating it into the target language. The system used predictive algorithms, which would guess which words should come next, based on the words and phrases it had “learned” before. These guesses often resulted in poor grammatical accuracy.
2016: Google Translate introduced neural machine translation (NMT), which outperformed phrase-based CAT tools and became the new commercial standard.
Why is translation technology important in today’s globalized world?
As the world keeps getting more connected, international consumers are increasingly looking for high-quality products and services that are culturally sensitive and adapted to their specific needs. At the same time, they demand seamless experiences that are as user-friendly and accessible as possible.
In the context of the information economy, adapting a product to local markets can mean having to deliver dozens of content types in multiple languages and to a wide range of audiences. Translation technology enables businesses not only to meet these challenges but also to maximize translation spend by increasing speed and quality while reducing cost.
In other words, translation technology allows companies to go global quickly, easily, and affordably by providing the tools they need to create, localize, manage, and publish content for audiences worldwide. Scalability, automation, intelligence, and accuracy become achievable and unlock business opportunities that were hardly imaginable with manual translation processes.
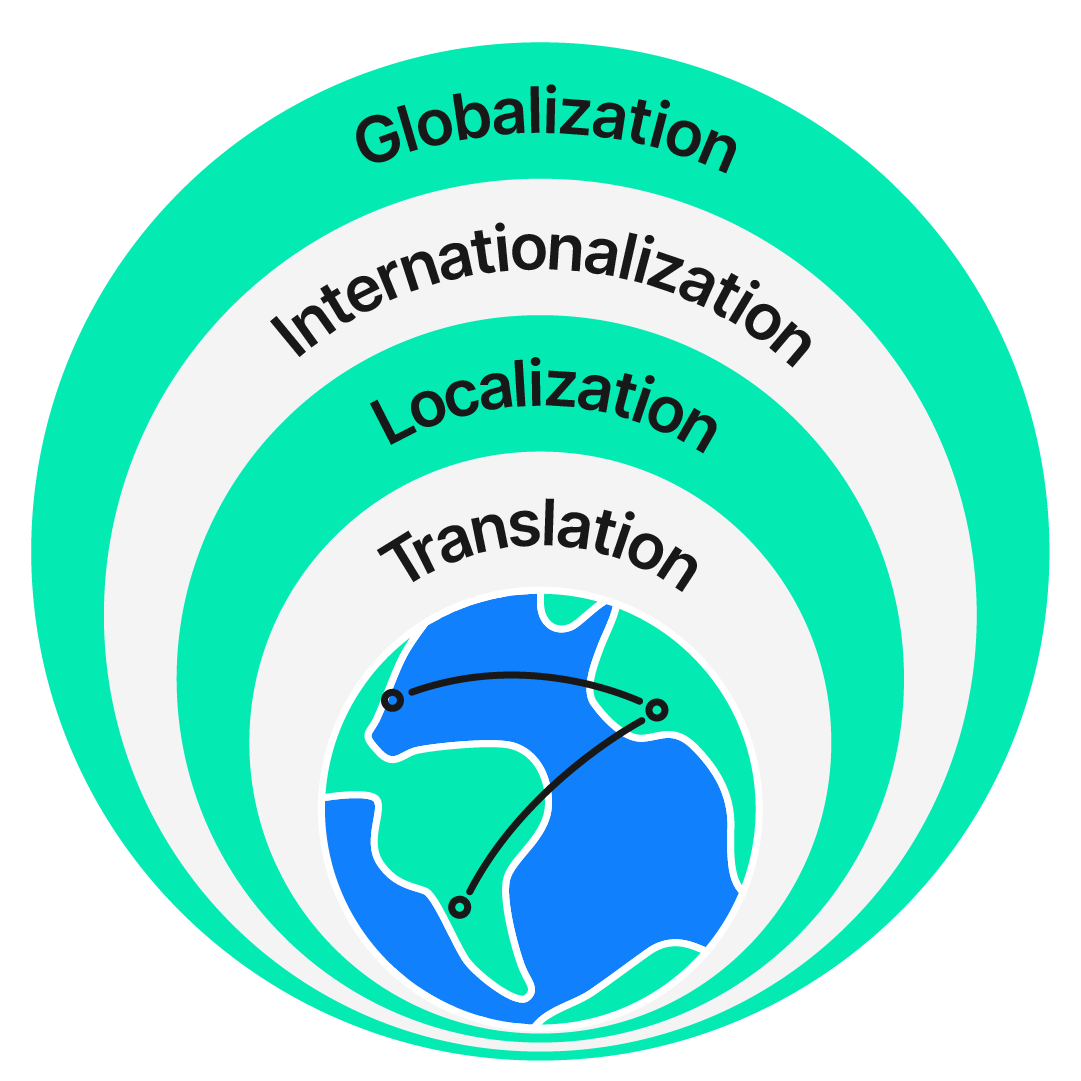
Translation is one of the key layers of business globalization
How does translation technology help businesses?
Today, translation technology tools helps businesses:
- Increase consistency across content by storing previous translations that can be reused or consulted in future projects
- Improve operational efficiency by automating translation management tasks
- Speed up time to market by enabling the production of more content in less time
Before we go into more depth on the various types of translation technology, let’s go back in time and examine how translation technology evolved.
On-demand webinar
Localization: Why you need it, and how to start
Learn from our expert panel how to prepare for global expansion, overcome common localization obstacles, and drive international growth.
The main types of translation technology
Modern translation technology is constantly evolving, with innovative solutions coming every year. What follows is a (non-exhaustive) list of the most popular translation technologies.
Computer-assisted translation tools
CAT tools are software applications created to support translators in their daily work. CAT tools use databases of previous translations (usually from a specific source language and target language) as well as frequency information, segmentation data, and a wealth of other resources to aid the translation process.
Visually, a CAT tool interface usually displays two columns or panels: One shows the source text, and the other displays the target text. Typically, the tool will segment the source text into chunks—sentences or paragraphs—to make it easier for the translator to keep track of the flow of information.
CAT tools usually have a large number of functions, such as:
- Translation memories, which allows translators to reuse previous translations
- Term bases or glossaries, which can be used to search for brand-specific or project-specific terminology
- The option to click through to secondary resources for additional context, such as images or comments left by other translators, the project manager, or other company stakeholders
- Advanced search and navigation tools
- Reports detailing how much of the translation has been completed
- Auto-completion of segments if they are an exact match to previously translated content
- Quality assurance tools to search for errors in the translation, such as untranslated segments, missing numbers, or instances where the same word has two different translations
- The possibility of generating a final translated document that automatically mirrors the original document’s format
- Integration with other translation technologies, such as neural machine translation engines
CAT tools have revolutionized translation technology, making it easier for companies to optimize the translation process and handle large amounts of content in a more efficient way, saving both time and money. For translators, the main benefit is that they can use the time saved on repetitive tasks to focus more on the translation itself.
CAT tools are also highly scalable and customizable, making them invaluable for any business seeking to streamline its translation process based on the specific needs of its content and target audience.
How do computer-assisted translation tools work?
Explore why growing businesses utilize a CAT tool for global expansion, what benefits it offers, and how to select the right one for your needs.
Machine translation software
Machine translation software is an automated system that allows for the production of translated content without human intervention. As described earlier in this guide, machine translation is not a new phenomenon. However, the advances in technology that have taken place in recent years have led to a rise in the use of MT. Machine translation differs from CAT tools in that it doesn’t rely on human input but produces translations entirely on its own.
Raw vs post-edited machine translation
The quality of machine translation output varies depending on factors, among which the language pair, subject matter of the original text, type of content, and the MT engine used.
Considering the above, companies can choose whether to use raw machine translation (i.e., completely unedited) or to hire human translators to refine the output, depending on their goals and needs. The latter is called machine translation post-editing (MTPE), and it can be either light or full.
Remember: For raw machine translation, it’s vital to use a state-of-the-art MT engine that is highly trained and powered by AI technology.
Choosing the best translation method for the right content type
Different types of texts will be more suitable for a lower level of editing. For example, a website’s FAQ page may require light editing; however, a press release that will directly impact the brand’s reputation should go through a full post-editing process.
By the same logic, sensitive content such as financial statements should always be handled by human translators. As a rule of thumb:
- Use raw machine translation for low-impact, quickly perishable, and unambiguous content. Think internal documentation, user-generated content like product reviews (for which consumers generally expect low quality), customer inquiries, or frequently amended feature or information updates.
- Apply light or full MTPE when your brand may suffer as a result of inaccuracies. It’s the case of product titles and descriptions (they tend to contain proper names and polysemous words), knowledge bases, press releases, etc.
- Leave it in the hands of human translators whenever top quality is key and there are no monetary or time constraints. Think legal, financial, or technical documents for which accuracy and consistency are paramount, as well as highly creative collateral designed to drive action.
Because machine translation is nowadays integrated into most modern CAT tools, you can aid the work of post-editors with CAT tools’ features such as glossaries, term bases, and translation memories, as well as brand books and style guides. This makes it very feasible to keep brand voice and key messaging consistent across cultures and languages with MTPE.
Machine translation explained
More and more businesses leverage machine translation to expand their global footprint more quickly. Learn how you can also make the most of this increasingly useful technology.
Translation management systems
Translation management system (TMS) is a software platform designed to facilitate translation projects by automating manual or repetitive tasks.
It streamlines the translation process from start to finish, creating a workflow from the initial request to project completion, and allowing users to plan, assign, and manage translation projects in an organized manner.
TMS solutions vary according to the needs of users (e.g. some are cloud-based and some are on-site). Nevertheless, in general, they all include a core set of features:
- Support for multiple languages and file formats
- A dashboard that displays a project’s status and provides access to essential tools in one place
- The option to automatically push (import) content into the TMS for translation and pull (export) it back after project completion
- The ability to streamline processes by adding users or importing existing translation requests from other systems for easier collaboration with third-party providers
- The ability to assign, modify, or release tasks at any point in the project
- A reporting function that provides a clear overview of progress across all projects
- User role management that maintains a separation between those who manage projects and those who translate them
- Real-time collaboration for active teamwork and reduced project turnaround time
- CAT-tool functionalities such as glossaries, termbases, and translation memories
- Machine translation capabilities that help speed up the translation process
- Out-of-the-box integrations and application programming interfaces (API) for connectivity with existing systems and other tools such as content management systems (CMS), UI design tools, version control systems, and more
The best TMS solutions are flexible enough to allow users to create their own workflows and customize the software according to the needs of specific projects, departments, and teams. They are highly scalable and grow together with your business.
What is a translation management system?
Learn what makes a translation management system and how it helps businesses seeking to expand globally translate content more quickly and efficiently.
How to choose the right translation technology provider
Because of the diversity of translation software out there, companies can pick and choose exactly what kinds of solutions work best for them. Different providers offer different benefits and drawbacks, and no two solutions are exactly the same.
To select the right one for your business, it’s important to consider—beyond key features—how well a given solution adapts to your translation technology strategy.
If the idea of developing a strategy for translation technology has never crossed your mind, you’re not alone, and it’s never too late to start. A well-crafted strategy will help you zero in on the right vendor for your needs.
Typically, a translation technology strategy includes the following components:
- Figuring out a way to weave the various tools already in use across departments. For example, if you use Salesforce as a CRM, Contentful as a CMS, and JIRA for project management, you might need a translation technology provider that offers integrations with all of them.
- Deciding who will be responsible for managing the solution.
- Assessing if there’s a technical team available internally to handle the configuration, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the system. If there isn’t, a solution that offers a plug-and-play setup and 24/7 customer support might be the best option.
- Defining which core functionalities your organization needs from its platform (e.g., machine translation, automated workflows, etc.)
- Establishing an implementation timeline and the budget available.
- Creating a system for tracking progress and success.
- Defining how the translation technology strategy fits into the bigger picture of overall organizational objectives for aspects like time to market, cost savings, revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and more.
The selection process should then include thorough research into each vendor’s offering, customer reviews, and the total cost of ownership.
There’s a one-stop shop for all your translation technology needs
It’s possible to get all of the above—and more—from the Phrase Localization Platform. An integrated suite of translation automation technology, Phrase is the complete localization solution for streamlining and optimizing the entire translation process in one place.
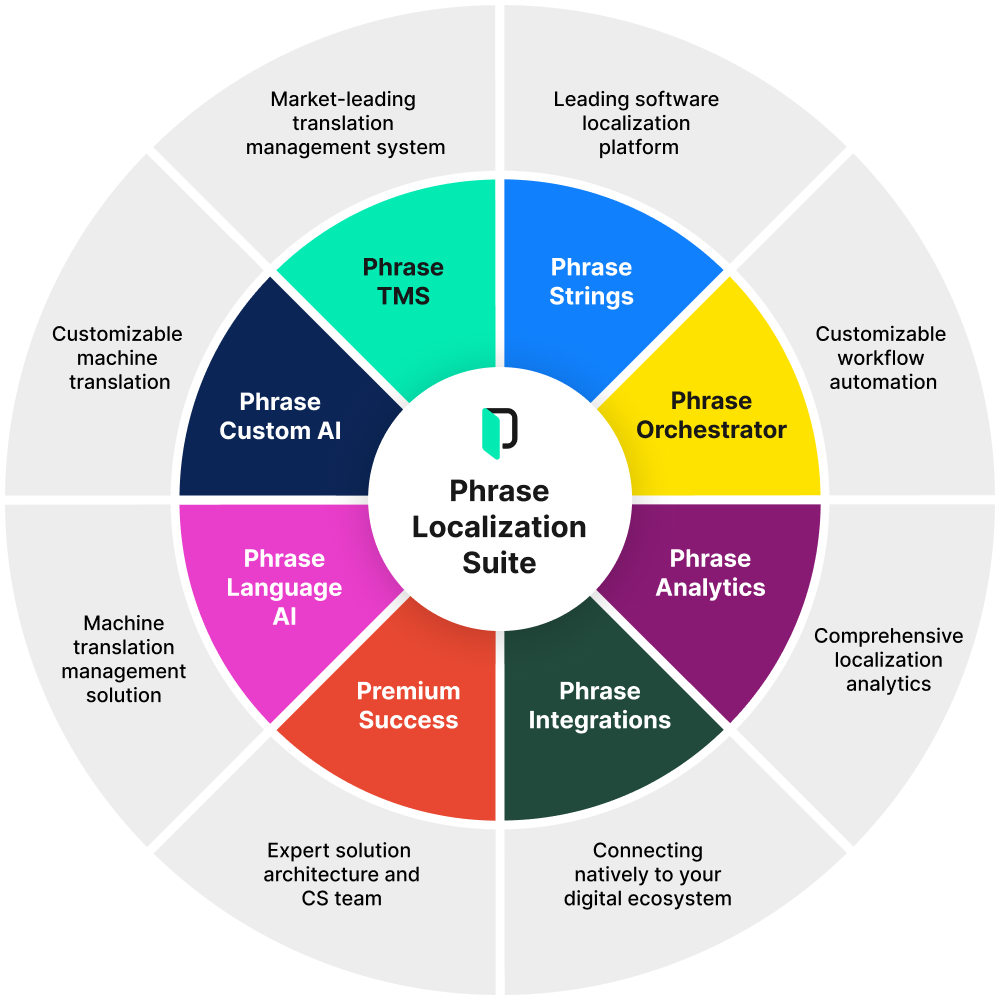
With the Phrase Localization Platform, you get access to:
- An enterprise-ready translation management system for end-to-end automation and optimization: Ideal for companies that want to centralize translation needs from multiple departments under one roof, Phrase TMS comes complete with a fully-featured CAT tool, native integrations, Support for 50+ files formats, and much more.
- A centralized string management platform for all your software copy: Developers, designers, product managers, and translators can work together efficiently from start to finish with Phrase Strings. It’s designed for digital product teams working in agile workflows and prioritizing quick turn-around times and automation.
- Versatile add-ons, like a workflow editor, Phrase Orchestrator, to quickly put together customized event-driven workflows and enable customization at scale, Phrase Language AI and Phrase NextMT for cutting-edge machine translation, and Phrase Analytics for tracking key translation management metrics.
The range of features and tools available in the Phrase Localization Platform is unparalleled and provides you with everything your organization needs to take its global initiatives to the next level:
- A visual editor for in-context previews of translated content to ensure more accurate translations
- Term base and translation memory capabilities to help translators stick to your preferred terminology and keep you from translating the same work twice
- Automated translation quality assurance to keep translations accurate and consistent
- 50+ integrations, from content management systems and marketing automation platforms to source code repositories and 3rd-party systems
- The ability to order professional translation services in one click and manage them from within a single platform
The future of translation technology
Translation tools are already much more nuanced than they were even just a couple of decades ago thanks to machine learning. Translation technology will only grow stronger as artificial intelligence continues to advance, and we’ll likely see even more features, integrations, and capabilities available in the years to come.
At Phrase, we’re already preparing for the next steps of this journey and continuing to build out our platform so that you can take advantage of all the latest advancements in translation technology.
With experts agreeing that the future of translation will combine human intelligence and AI-powered machine translation to produce the best results, we’ll likely transition from computer-assisted human translation to human-assisted computer translation. Machine-translation post-editing will ensure that AI-generated translations are accurate and fluent, while human translators will make the final creative changes to cater to specific audiences.
Whatever the future may bring, you can feel confident that Phrase will be there to help make sure your global expansion strategy is successful. The horizon looks bright, and we can’t wait to help you reach it.
Speak with an expert
Want to learn how our solutions can help you unlock global opportunity? We’d be happy to show you around the Phrase Localization Platform and answer any questions you may have.




